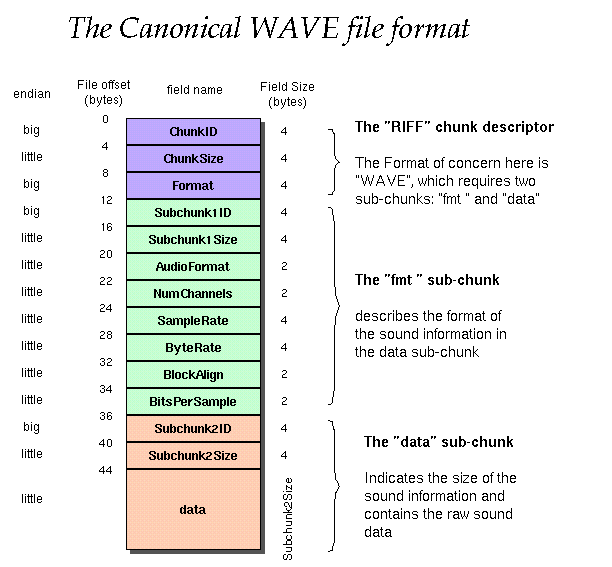
Wave文件是用于多媒体文件存储的Microsoft RIFF(Resource Interchange File Format 资源交换档案标准)规范的子集之一。一个RIFF文件以一个文件头(File Header)开始,接着是一系列数据块(data chunk)。一个Wave文件常常是一个带有一个单“WAVE”块的RIFF文件。该“WAVE”chunk由两个子快组成,一个“fmt”chunk用于详细说明数据格式,一个“data”chunk包含实际的样本数据。这种形式我们称为规范形式。
| Offset | Size | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4 | ChunkID | ASCII码0x52494646对应字母RIFF |
| 4 | 4 | ChunkSize | 块大小是指除去ChunkID与ChunkSize的剩余部分有多少字节数据,注意:小尾字节序数。Value=36 + SubChunk2Size 或者 Value = 4 + (8 + SubChunk1Size) + (8 + SubChunk2Size)。 |
| 8 | 4 | Format | ASCII码0x57415645对应字母WAVE。该块由两个子快组成,一个fmt chunk用于详细说明数据格式,一个data chunk包含实际的样本数据。 |
| 12 | 4 | Subchunk1ID | ASCII码0x666d7420对应字母fmt。 |
| 16 | 4 | Subchunk1Size | 如果文件采用PCM编码,则该子块剩余字节数为16。 |
| 20 | 2 | AudioFormat | 音频数据格式。如果文件采用PCM编码(线性量化),则AudioFormat=1(0x0001表示PCM数据)。AudioFormat代表不同的压缩方式。 |
| 22 | 2 | NumChannels | 声道数,单声道(Mono)为1, 双声道(Stereo)为 2。 |
| 24 | 4 | SampleRate | 取样率,例:44.1kHz,48kHz。 |
| 28 | 4 | ByteRate | 传输速率,单位:Byte/s。 Value = SampleRate ∗ NumChannels ∗ BitsPerSample / 8 |
| 32 | 2 | BlockAlign | 一个样点(包含所有声道)的字节数。Value = NumChannels ∗ BitsPerSample / 8 |
| 34 | 2 | BitsPerSample | 每个采样点(的幅值)对应的比特编码位数(8 or 16)。 |
| 2 | ExtraParamSize | 如果采用PCM编码,该值不存在。 | |
| X | ExtraParams | 用于存储其他参数。如果采用PCM编码,该值不存在。 | |
| 36 | 4 | Subchunk2ID | ASCII码0x64617461对应字母data。 |
| 40 | 4 | Subchunk2Size | 实际样本数据的大小(单位:字节)。Value = NumSamples ∗ NumChannels ∗ BitsPerSample / 8 |
| 44 | * | Data | 实际的音频数据 。 |
As an example, here are the opening 72 bytes of a WAVE file with bytes shown as hexadecimal numbers:
52 49 46 46 24 08 00 00 57 41 56 45 66 6d 74 20 10 00 00 00 01 00 02 00
22 56 00 00 88 58 01 00 04 00 10 00 64 61 74 61 00 08 00 00 00 00 00 00
24 17 1e f3 3c 13 3c 14 16 f9 18 f9 34 e7 23 a6 3c f2 24 f2 11 ce 1a 0d
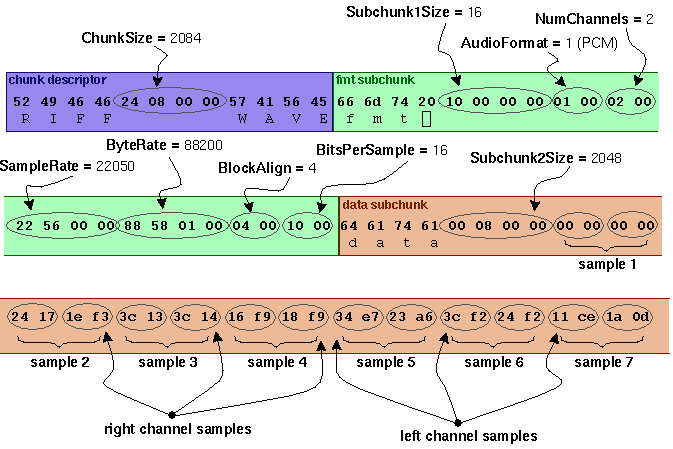
上图所示例子,该WAVE文件采用PCM编码。该音频具有双声道,每个样点进行16位量化编码,双声道的一个样点占4字节,存储顺序是每个样点的左右声道交替存储。
Here is the interpretation of these bytes as a WAVE soundfile:
Notes:
- The default byte ordering assumed for WAVE data files is little-endian. Files written using the big-endian byte ordering scheme have the identifier RIFX instead of RIFF.
- The sample data must end on an even byte boundary. Whatever that means.
- 8-bit samples are stored as unsigned bytes, ranging from 0 to 255. 16-bit samples are stored as 2’s-complement signed integers, ranging from -32768 to 32767.
- There may be additional subchunks in a Wave data stream. If so, each will have a char[4] SubChunkID, and unsigned long SubChunkSize, and SubChunkSize amount of data.
- RIFF stands for Resource Interchange File Format.
General discussion of RIFF files:
Multimedia applications require the storage and management of a wide variety of data, including bitmaps, audio data, video data, and peripheral device control information. RIFF provides a way to store all these varied types of data. The type of data a RIFF file contains is indicated by the file extension. Examples of data that may be stored in RIFF files are:
- Audio/visual interleaved data (.AVI)
- Waveform data (.WAV)
- Bitmapped data (.RDI)
- MIDI information (.RMI)
- Color palette (.PAL)
- Multimedia movie (.RMN)
- Animated cursor (.ANI)
- A bundle of other RIFF files (.BND)
NOTE: At this point, AVI files are the only type of RIFF files that have been fully implemented using the current RIFF specification. Although WAV files have been implemented, these files are very simple, and their developers typically use an older specification in constructing them.
Q & A
-
8bit与16bit样值的二进制编码表示是一样的吗?
8bit样值以无符号形式存储,取值范围0-255 。而16bit样值以有符号的补码形式存储,取值范围-32768 to 32767。
-
现有的WAV支持哪几种音频压缩方法
| AudioFormat | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 (0x0000) | Unknown |
| 1 (0x0001) | PCM/uncompressed |
| 2 (0x0002) | Microsoft ADPCM |
| 6 (0x0006) | ITU G.711 a-law |
| 7 (0x0007) | ITU G.711 µ-law |
| 17 (0x0011) | IMA ADPCM |
| 20 (0x0016) | ITU G.723 ADPCM (Yamaha) |
| 49 (0x0031) | ITU G.721 ADPCM |
| 80 (0x0050) | MPEG |
| 65,536 (0xFFFF) | Experimental |